TWIRL, designed by Zaha Hadid, is located in
an 18th century courtyard in Italy. The installation emphasizes making use of
arches and curves to distort the sense of space.
Picture 1 – Perspective
Picture 2 – Effects of Fluorescent Light
Picture 3 – Floor Plan
INTRODUCTION
In this project, I used Rhino &
Grasshopper to recreate the model of TWIRL based on the information I got about
the original design.
MODELING
1. Curves on the Horizontal Surfaces
Because curves on the horizontal surface are relatively irregular, I divided them into several groups based on the curvatures. For the arches in each group at the right bottom, I created three curves linking the starting, mid, and ending points of originally designed curves in Rhino. And, by using DIVIDE and INTERPOLATE, I created designed curves through several sets of division points. While, for the bi-arches at the left top, I used similar method but drawing more curves to make a better control. Moreover, due to NUMBER SLIDER I added, numbers of curves in each groups are controlled.
Screenshot – 1
2. A Controlled Curved Surface
First, I drew a circle according to the radial
point of construction in Rhino. Then, based on that, seven circles with different radius and height are created by using MOVE and
SCALE. Through this group of circles, a curved surface was created. Furthermore,
by changing the values of NUMBER SLIDER, the shape and height of this surface
can be controlled.
Screenshot
– 2
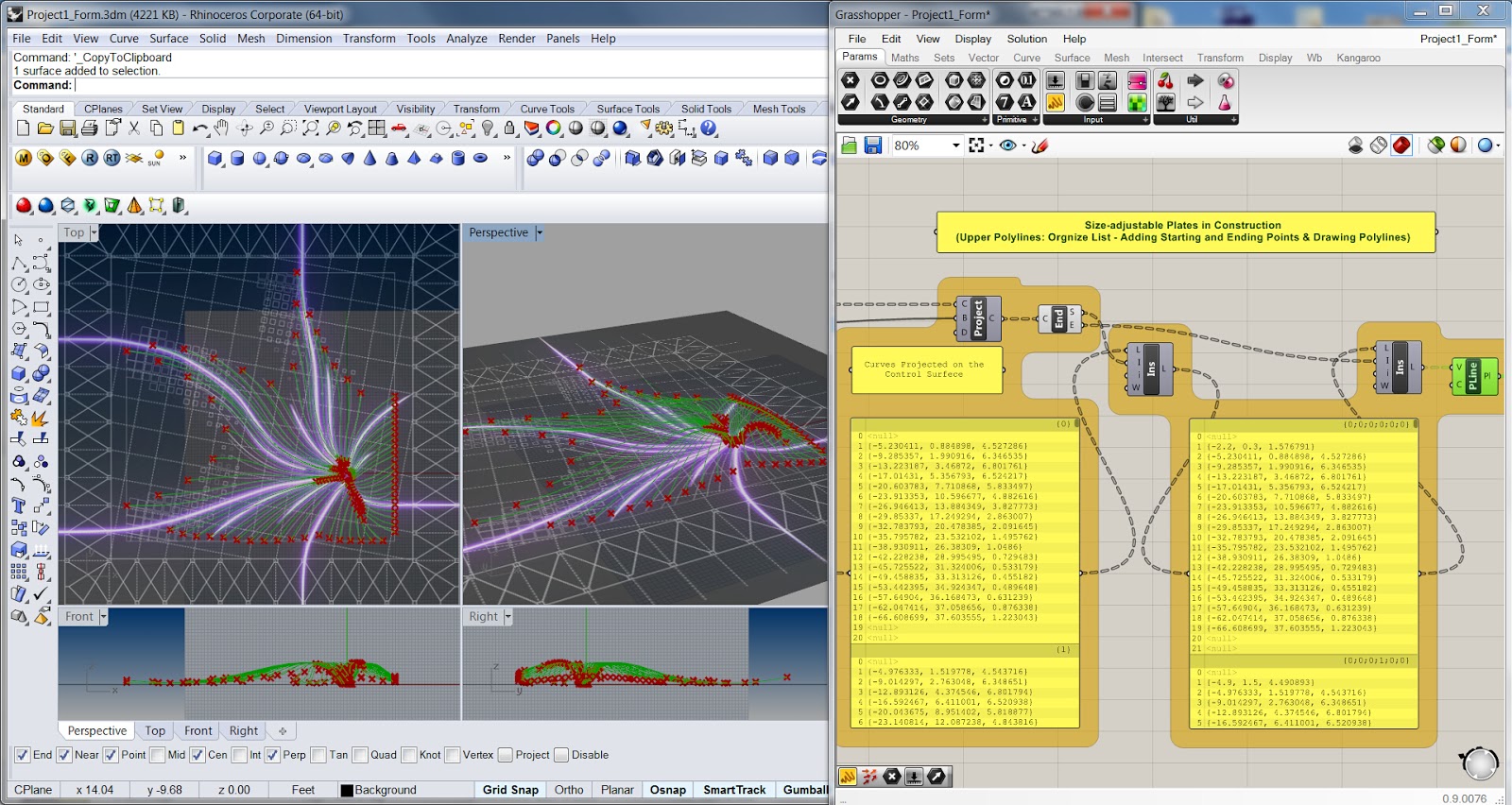
3. Size-adjustable Plates in Construction
Because in reality, lots of planar ceramic sheets, rather than several whole curved sheets, are used
for construction. I want to create these quadrangular plates by locating and
linking points in both the horizontal and curved surfaces.
3.1 Vertical Lines
First, by using RANGE & EXPRESSION, I created
21 circles with same intervals at the horizontal surface. These circles crossed with the curves formed in step 1. Then, lots of intersection points
are created. By linking these points and points projected on the curved surface,
vertical lines are formed. While, changing the radius of these circles means regulating
the size of each ceramic sheets.
Screenshot – 3
Screenshot – 4
Screenshot – 5
3.2 Upper Poly-lines
Most curves on the horizontal surface may
not across with outer circles due to their lengths, so
some parts of the data list show blanks. By changing these parts into ‘null’ and
regrouping data, main parts of upper poly-lines are created. After that, by inserting
values of starting and ending points into the list, the whole upper poly-lines
of vertical surfaces are created.
Screenshot – 6
Screenshot – 7
4. Making Surfaces
By projecting upper poly-lines on the
horizontal surface, bottom poly-lines of designed surfaces are created. After lines
linking with starting and ending points of both poly-lines are formed, four edge
curves are finished. By using EDGE SURFACE, all vertical surfaces are created.
Screenshot – 8
5. Physically-based Model
Because of the limitation from my computer’s hardware,
I just choose parts of the model to show physical changes.By using KANGAROO, WEAVEBIRD, and UNARYFORCE,a horizontal force added to a set of designed surfaces.
Screenshot – 9
Screenshot – 10
6. Analyses
6.1 Curvature Analysis
By baking the surfaces, curvatures can be analyzed
in Rhino.
Screenshot – 11
6.2 Area Analysis
Summing up the areas of vertical sheets
which help to calculate the cost.
Screenshot – 12
RENDERING
Picture 4 – Perspective 1
Picture 5 – Perspective 2
Picture 6 – Elevation